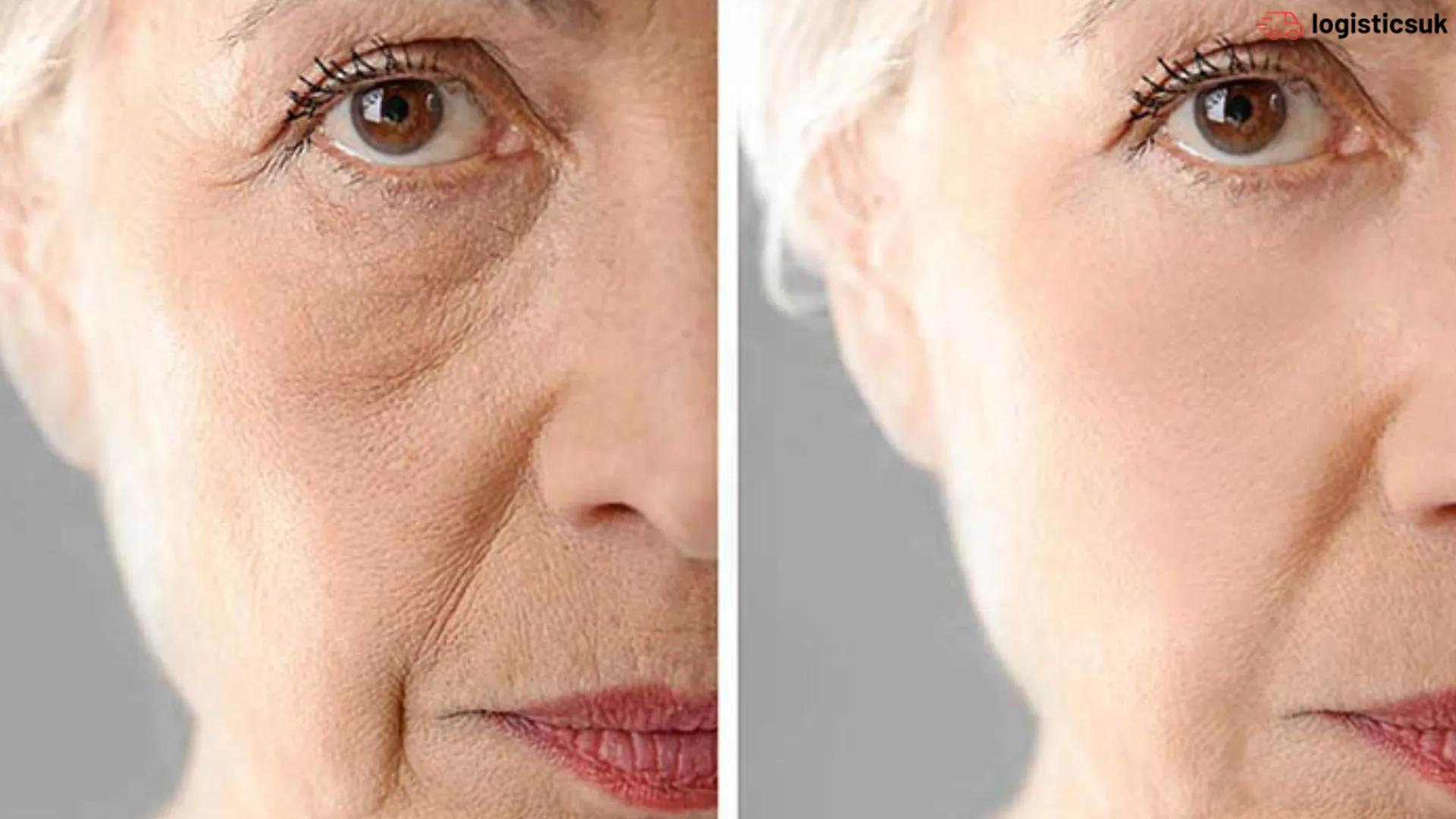
Skin laxity, called sagging or loose skin, is a natural aging process. Over time, the skin loses its firmness and elasticity, leading to wrinkles and a less youthful appearance. While aging is the primary cause of loss of skin elasticity, various factors contribute. So, let’s delve into the causes of skin laxity, explore preventive measures, and discuss the available treatments.
Factors Leading to Skin Laxity Decline
Collagen Depletion
Collagen, the most abundant protein in the human body, is crucial in maintaining skin elasticity and plays a significant role in skin rejuvenation. It provides structural support, helping the skin to stay firm and supple.
As we age, the body’s natural collagen production decreases, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and contributing to the need for skin rejuvenation techniques. Sun exposure, smoking, and poor nutrition can accelerate collagen depletion.
Elastin Breakdown
Elastin is another essential protein responsible for skin elasticity. It allows the skin to snap back into place after stretching. Over time, the breakdown of elastin fibers results in reduced skin elasticity, leading to the development of loose skin. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun significantly contributes to elastin degradation, emphasizing the importance of sun protection in preventing skin laxity.
Other Causes of Skin Laxity
- Genetics can significantly impact the skin’s resilience and tendency to develop loose skin. An individual’s genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining skin characteristics, including its ability to retain elasticity and its response to skin aging.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, especially during menopause, can decrease collagen production and skin laxity.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to environmental pollutants, harsh weather conditions, and free radicals can contribute to premature aging and skin laxity, making skin tightening treatments more appealing.
- Lifestyle Choices: Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a poor diet can accelerate the aging process and contribute to skin laxity.
Unveiling the Role of Collagen in Skin Health
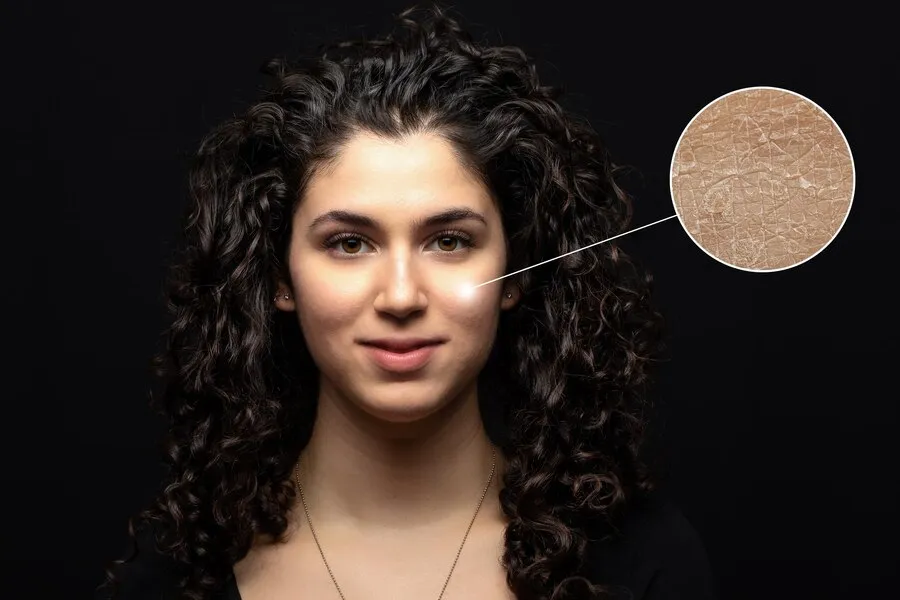

Collagen is a fibrous protein that provides strength and structure to various tissues in the body, including the skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments. In skin health, collagen is crucial for maintaining firmness and elasticity. It forms a network of fibers that supports the skin and helps it resist stretching.
As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin, which may prompt the need for cosmetic interventions. UV radiation, pollution, and other environmental factors can further accelerate collagen breakdown, exacerbating skin aging. Various skincare products and treatments aim to stimulate collagen production or replenish it through external sources to address collagen loss.
Deciphering Elastin: The Key to Skin Elasticity
Elastin is a protein that works with collagen to maintain skin elasticity, which is essential for effective skin tightening. While collagen provides structural support, elastin allows the skin to stretch and return to its original shape. Elastin fibers are responsible for the skin’s ability to bounce back after movements like smiling or frowning, contributing to skin tightening.
Similar to collagen, elastin production decreases with age. UV radiation, smoking, and environmental factors contribute to the breakdown of elastin fibers, leading to skin sagging and wrinkling. Protecting the skin from sun exposure and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help preserve elastin, maintain skin elasticity, and promote effective skin care.
Additional Contributors to Skin Laxity Beyond Collagen and Elastin
In addition to collagen and elastin depletion, several other factors contribute to skin laxity:
- Loss of Subcutaneous Fat:
The layer of fat beneath the skin, known as subcutaneous fat, provides volume and support. As this fat diminishes with age, the skin may sag and lose its plumpness, prompting individuals to consider cosmetic options like a facelift.
- Gravity plays a role in skin aging, causing skin to sag over time and lose its youthful appearance.
Gravity exerts a constant force on the body, causing tissues to droop over time. Areas with less underlying support, such as the cheeks and neck, are particularly prone to gravity’s effects.
- Repeated Facial Expressions:
When repeated over the years, facial movements and expressions can contribute to forming fine lines and wrinkles, which many seek to address through skin tightening treatments. Dynamic wrinkles, often caused by muscle contractions, can become more apparent with age.
Strategies for Warding Off the Aging Process in Your Skin
While it’s impossible to stop the aging process, certain lifestyle choices and skincare practices can help slow down skin aging and prevent premature skin laxity:
- Sun Protection:
UV radiation is a major contributor to collagen and elastin breakdown. Use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and limit sun exposure to maintain healthy skin.
- Healthy Diet:
A well-balanced diet of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports overall skin health. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids improve skin elasticity.
- Hydration:
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining skin suppleness. Drink enough water to keep your skin hydrated and prevent dryness, which can contribute to premature aging.
- Avoid Smoking:
Smoking accelerates the aging process and contributes to the breakdown of collagen and elastin. Quitting smoking can significantly improve skin health.
- Topical Treatments:
Use skincare products containing ingredients like retinoids, peptides, and hyaluronic acid. These can promote collagen production, improve skin texture, and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
Enhancing Skin Firmness: Available Treatment Approaches
When preventive measures are insufficient, various treatments can help improve skin laxity. These treatments can be broadly categorized into non-surgical and surgical procedures.
Non-Invasive Methods to Address Skin Laxity
- Dermal Fillers:
Dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid-based injections, can add volume to areas with sagging skin, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and restoring a more youthful contour.
- Botox Injections:
Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections temporarily relax facial muscles, reducing the appearance of dynamic wrinkles. While not a direct treatment for skin laxity, Botox can improve the face’s overall appearance.
- Ultherapy:
Ultherapy is a non-invasive procedure that uses focused ultrasound energy to improve collagen production. It can lift and tighten the skin on the face, neck, and décolletage.
- Laser and Radiofrequency Therapies:
These treatments use energy to stimulate collagen production and tighten the skin. They can improve skin texture, reduce fine lines, and enhance skin tone.
Also Read:
Surgical Approaches for Improving Skin Firmness
- Facelift:
A facelift is a surgical procedure that addresses sagging and loose skin on the face and neck. It involves lifting and repositioning facial tissues to create a more youthful appearance.
- Neck Lift:
Like a facelift, a neck lift specifically targets sagging skin and excess fat in the neck area, providing a more defined jawline and smoother neck contour.
- Brow Lift:
A brow lift, or forehead lift, addresses sagging eyebrows and forehead skin. It can rejuvenate the upper face, reducing wrinkles and restoring youthful expression.
- Eyelid Surgery (Blepharoplasty):
Eyelid surgery removes excess skin and fat from the upper and lower eyelids. It can improve droopy eyelids and reduce under-eye bags.
Final Thought
Skin laxity is a natural part of aging, influenced by factors such as collagen and elastin depletion, genetics, and environmental exposures. While it’s impossible to completely halt aging, adopting a healthy lifestyle and skincare practices can help prevent premature skin laxity.
Various non-surgical and surgical treatments are available when preventive measures are insufficient to improve skin laxity and restore a youthful appearance. Consultation with a dermatologist or plastic surgeon can help determine the most suitable approach based on individual needs and concerns.