Table of Contents
Logistics is facing a rapid technological shift as artificial intelligence (AI) becomes essential, not optional. In 2025, the global AI in logistics market is expected to surge to $20.8 billion, reflecting a 45.6 % compound annual growth rate (CAGR) since 2020, according to McKinsey data. AI now shapes route planning, demand forecasting, risk management, and customer experience across fulfilment networks.
However, trust in AI remains complicated. A 2025 global study involving 48,340 respondents across 47 countries shows that many workers use AI without organisational oversight, with 57 % hiding AI use from bosses and only 47 % receiving formal training.
In logistics, this tension between benefit and risk matters because the supply chain involves high-value assets and tight schedules. We need to understand how AI improves performance and where it can introduce risk. In this article, we explore fact-based insights into AI adoption, common risks, mitigation strategies, and what truly builds trust in AI within logistics. We conclude with actionable guidance that helps logistics leaders decide when AI is trustworthy and what they must do to keep risk manageable.
AI Adoption in Logistics: Real Numbers and Trends
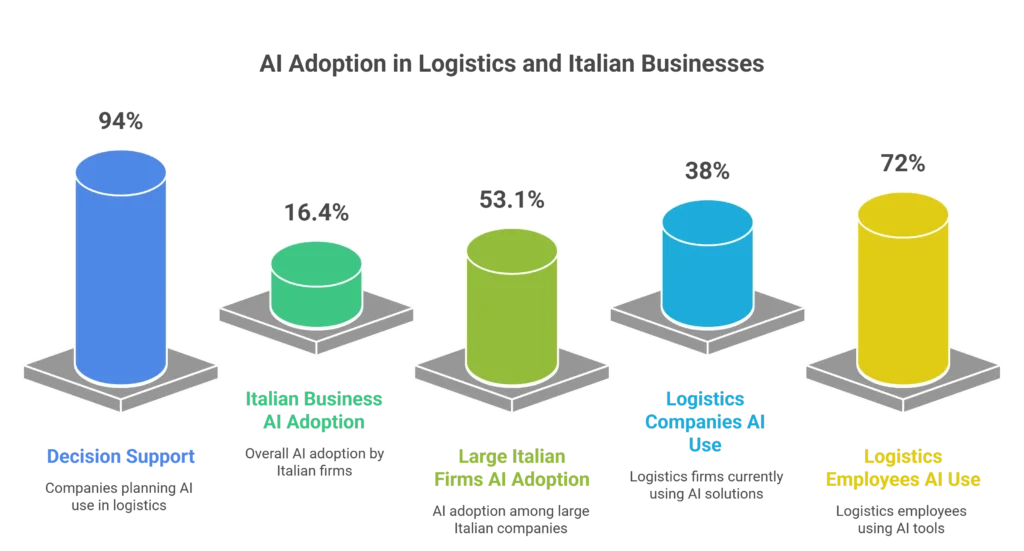
AI adoption in logistics is strong but uneven. A 2025 supply chain survey shows 94 % of companies plan to use AI for decision support, with demand forecasting and customer-service enhancements close behind.
Across broader business sectors, Italian firms using AI have doubled to 16.4 % in 2025, with larger companies leading at 53.1 % adoption.
In logistics specifically:
- 38 % of logistics companies already use AI solutions, improving transit times and fuel consumption.
- 72 % of logistics employees use AI tools, ahead of the cross-industry average.
These figures make clear that logistics is one of the leading sectors for AI uptake. Yet adoption rates vary by company size, digital maturity, and internal skills. Larger, digitally mature firms outpace smaller operations in deploying AI for optimisation, visibility, and predictive insights. They learned the hard way that 87% of consumers wouldn’t consider businesses rated below 3 stars.
The Measurable Benefits of AI in Logistics
Concrete Improvements in Performance
AI’s value in logistics is measurable. According to reports:
- AI-driven route optimisation reduces fuel use by up to 15 %.
- Supply chains using AI show 67 % better risk reduction and optimisation.
- Forecasting systems can cut forecasting errors by 20–50 %.
These improvements translate into savings on fuel, labour, and warehousing costs, and often faster delivery times.
Benefits Across Operations
| Area of Logistics | AI Benefit | Measured Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Route optimisation | Fuel reduction | 15 % reduction in fuel use |
| Supply chain risk | Risk mitigation | 67 % better optimisation |
| Forecasting | Error reduction | 20–50 % fewer forecasting errors |
AI gives logistics firms sharper decision signals and operational efficiencies that manual processes can’t match. The result is better cost control and more predictable performance.
How Businesses Can Reduce AI Risks
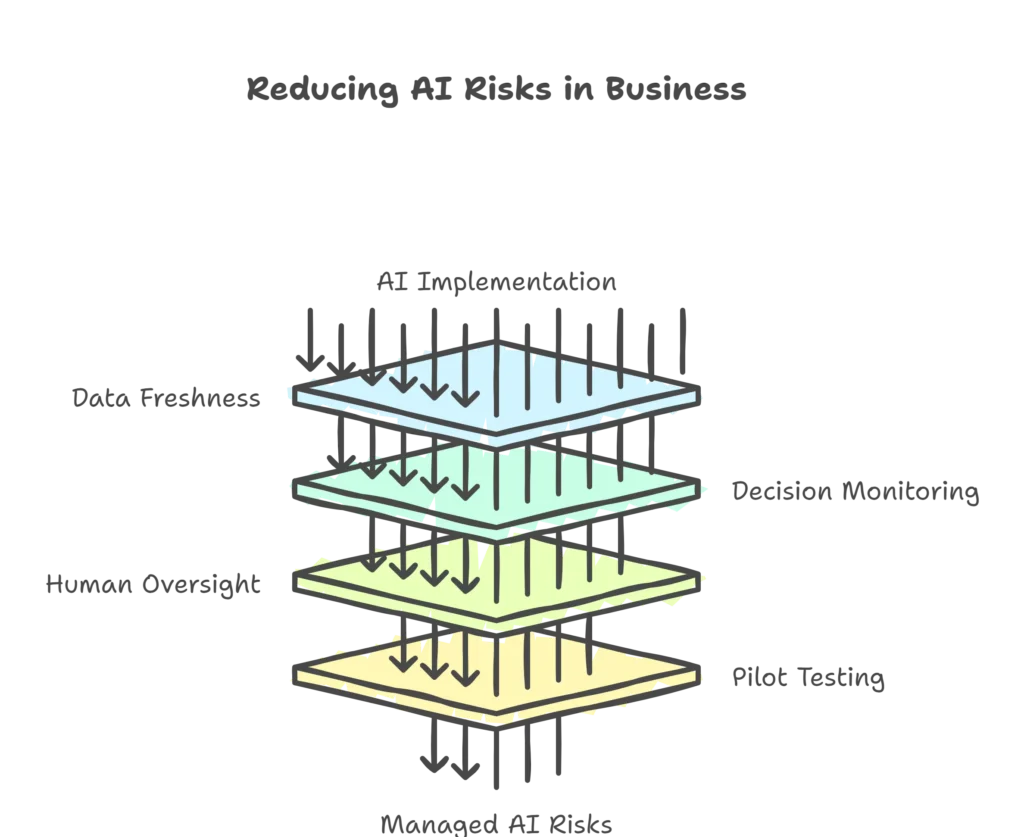
Keep Data Fresh
Regularly update addresses, supplier details, and warehouse information. Assign a team to check data weekly. Do not assume the AI is self-correcting.
Monitor AI Decisions
Do not let the system run unchecked. Review its suggestions. If it recommends routes that look odd, flag them before they become routine errors.
Combine Human Oversight
AI should guide, not replace, human decision-making. Drivers and managers know when something feels wrong. Encourage feedback loops so humans can override AI mistakes.
Test Before Scaling
Roll out new AI tools in small pilots. Track error rates and customer complaints. Only expand when you know the risks are manageable.
The Real Risks of AI in Logistics
Trust Deficits and Organisational Blind Spots
A major risk in logistics isn’t just the technology, but how it’s used. The 2025 trust study shows many employees rely on AI without training or oversight, creating blind spots that can damage data security and compliance. )
Additional concerns include:
- Shadow AI: AI tools used outside approved systems, leading to data leakage or compliance risks.
- Lack of AI governance: Few logistics firms have formal policies guiding AI use, opening the door to inconsistent outcomes and legal liabilities.
Non-Technical Risks
Risk in logistics also comes from overreliance on AI outputs without human verification. Misdeclared dangerous goods have triggered cargo fires; AI is now being deployed to spot risky cargo in bookings because of these safety issues. Learn more in our article on How Industrial Packaging Automation Reduces Material Handling Costs.
Action Steps for Logistics Teams
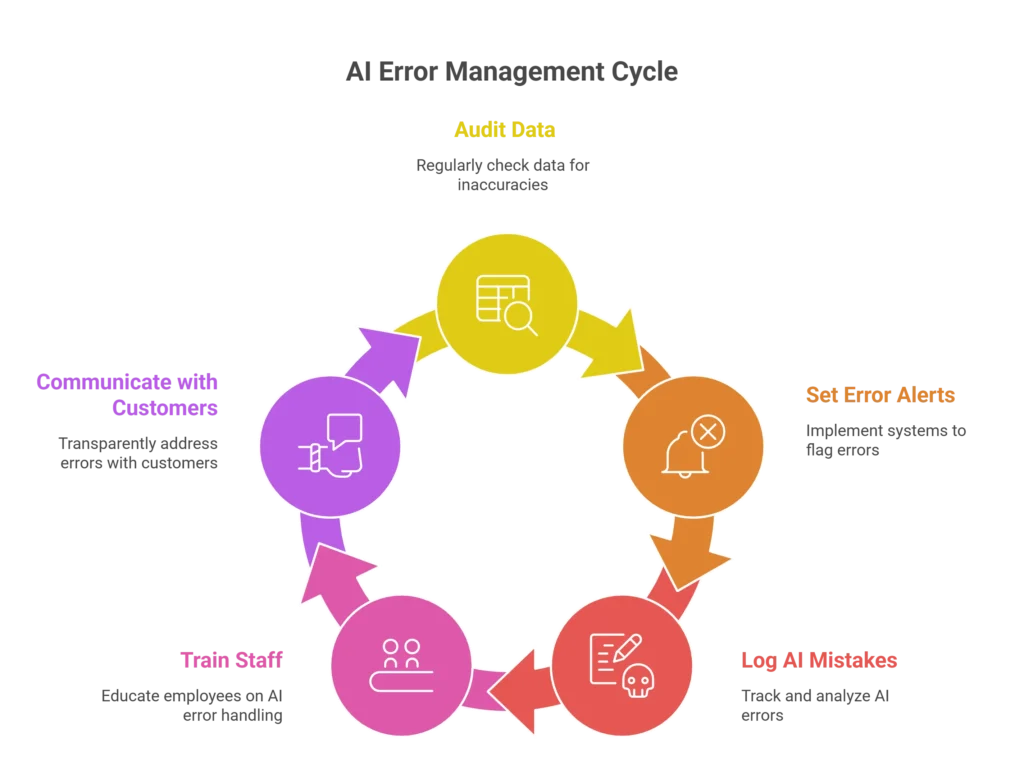
- Audit Data Monthly: Check addresses, supplier info, and customer details.
- Set Error Alerts: Create systems that flag repeated failed deliveries.
- Log AI Mistakes: Track when AI suggestions lead to errors. Use this data to refine or retrain the system.
- Train Staff: Teach employees how to spot AI mistakes and when to override them.
- Communicate with Customers: If mistakes happen, admit them quickly. Transparency rebuilds trust faster than silence.
Building Trust: Practical Steps for Logistics Leaders
Governance and Training Go Together
Trustworthy AI in logistics depends on clear governance and employee skills. Firms must:
- Establish AI usage policies that cover data use, compliance, and model validation.
- Implement formal training programmes so logistics personnel understand AI limitations and strengths.
The 2025 trust study highlights that widespread usage without oversight undermines confidence and increases risk.
Structured Risk Management
Risk management frameworks should embed AI oversight into logistics risk registers. This includes:
- Ongoing performance monitoring of AI models.
- Humans check for safety-critical decisions.
- Data-protection standards aligned with GDPR or local laws.
Bottom Line
AI is reshaping logistics with measurable efficiencies in routing, forecasting, and risk management. Today’s data shows real benefits, but also real risks if AI is adopted without governance and oversight. Logistics firms must strengthen AI policies, invest in workforce training, and embed risk management to build actionable trust. Only with these steps can AI in logistics be both powerful and reliable, delivering improved performance without unmanaged risk.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute legal, operational, or professional advice.


